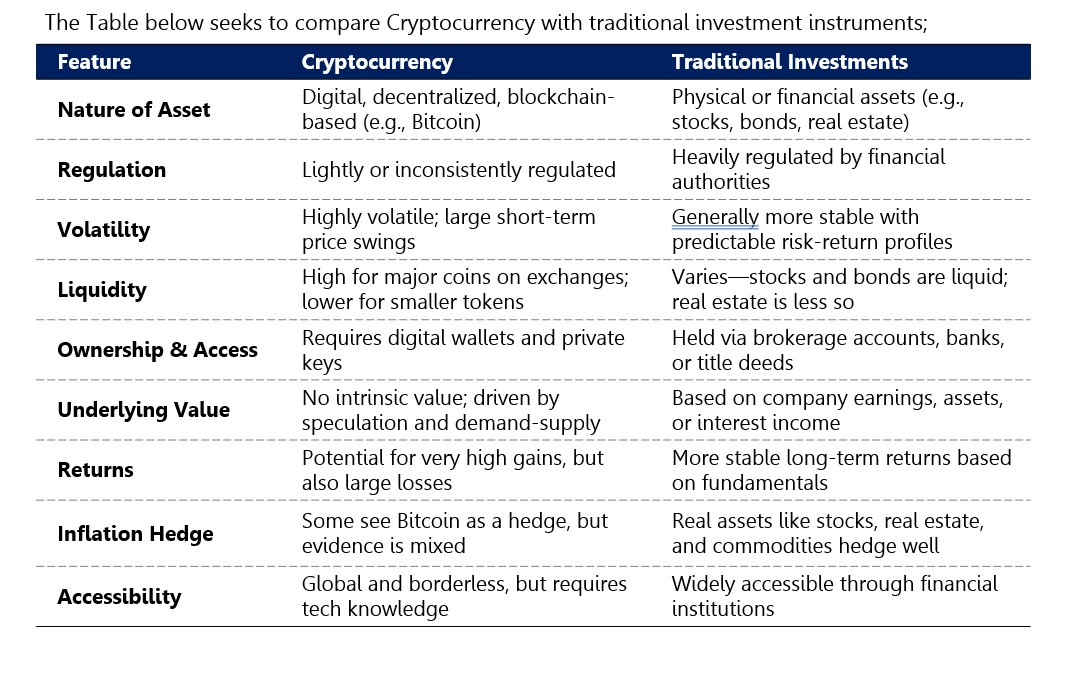
Cryptocurrency (Crypto) is a form of digital currency that uses cryptographic techniques to secure the transmission and storage of data and to control the creation of new units. Unlike physical cash, cryptocurrencies exist solely in digital form.
Owning Crypto means holding a private key that allows you to transfer units from one party to another across a decentralized network – one that does not rely on a central authority or intermediary and is maintained by a distributed community. Every transaction is recorded and updated on a blockchain, ensuring accuracy and bolstering trust among participants.
Since the launch of Bitcoin (the first and most widely used cryptocurrency) in 2009, thousands of cryptocurrencies have emerged, each offering different features and use cases. While cryptocurrencies have existed for over a decade, the broader applications of blockchain technology, especially in financial services, are still evolving, with significant innovation and adoption expected in the years ahead.
Benefits of Cryptocurrency
1.High growth potential – Cryptocurrencies have historically offered investors significantly higher returns compared to traditional investments, often over shorter timeframes. For example, Bitcoin rose from US$0.90 in 2010 to around US$105,816 by mid-June 2025.
2.Decentralization and Financial Independence – Unlike traditional financial systems, cryptocurrencies are not controlled by any single government or institution. This offers greater autonomy, enabling individuals to manage wealth, conduct transactions, and access services without centralized intermediaries.
3.Enhanced Transparency – Crypto transactions are recorded on a public blockchain ledger, strengthening network security and trust. This transparency gives participants real-time access to accurate information and helps enhance confidence in the system.
Risks Associated With Cryptocurrency
1.Price Volatility – Cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate rapidly and unpredictably due to speculative trading and pump-and-dump schemes. Because returns are driven by demand and supply dynamics, they are often uncertain and cannot be guaranteed.
2.Cyberattacks – Cryptocurrency hackers may steal private keys and gain access to users’ assets, often resulting in permanent and usually irrecoverable losses. High-profile incidents include the 2018 hacks of Coincheck and BitGrail, which led to losses of US$534 million and US$195 million, respectively.
3.Lack of Consumer Protection – Unlike traditional financial systems, cryptocurrencies typically lack regulatory oversight and formal consumer safeguards. If a Crypto trading platform (CTP) or wallet provider fails or goes bankrupt, investors may have no legal recourse to recover their funds.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
The information contained in this blog is being provided for educational purposes only and does not constitute a recommendation from any Bora Capital Advisors entity to the recipient. Bora Capital Advisors is not providing any financial, economic, legal, investment, accounting, or tax advice through this blog to its recipient. This report reflects the views and opinions of Bora Capital Advisors Ltd, and is provided for information purposes only. Although the information provided in the market review and outlook section is, to the best of our knowledge and belief correct, Bora Capital Advisors Ltd, its directors, employees and related parties accept no liability or responsibility for any loss, damage, claim or expense suffered or incurred by any party as a result of reliance on the information provided and opinions expressed in this report, except as required by law. The portfolio performance data represented in this report represents past performance and does not guarantee future performance or results.




